For several years, landfills were the most commonly used method of waste disposal. However, the technique has reduced in popularity because of the negative impacts on the environment. Landfills are significant sources of air and water pollution. Landfills emit methane, dioxin, and leachate as by-products when the waste is broken down. These products are extreme contaminants which, when left untreated, can cause damage to the soil, plants, and water sources. As a response to the downfall of landfills as a mode of waste disposal, waste to energy plants were established. There are several wastes to energy plants in different parts of the globe, like MoreGreen, whose information can be obtained from this website.
What is a waste to energy plants?
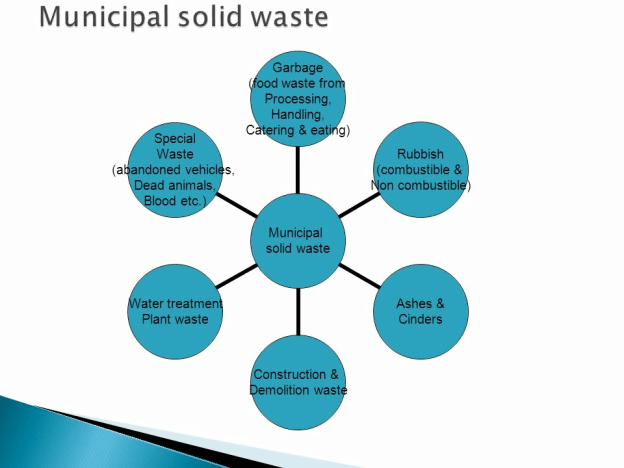
Waste to energy plants are facilities where municipal solid wastes are converted into energy that can be used as electricity or heat. Municipal solid waste is a term used to describe the regular garbage or trash thrown away from households.
These forms of wastes can include packaging items, grass clippings, food wastes, bottles, appliances, waste paint, batteries, clothes, or furniture. The task of collecting and developing disposal techniques for these wastes falls in the arms of the municipality.
Waste to energy techniques

There are two categories of waste to energy techniques.
1. Thermal techniques
These are techniques that employ high temperatures of heat. The methods under this category are:
Incineration- the burning down of wastes in plants, barrels, or heaps.
Pyrolysis- this is a process of degrading organic wastes in very high temperatures in the absence of oxygen.
Hydro pyrolysis- this is a process of degrading organic substances in high temperatures in the presence of water.
Thermal depolymerization- this is a method of converting waste into liquid light energy in the presence of very high temperatures.
Gasification- this is the proves of converting low-value feedstock wastes into high volume usable products. The primary end product of the process of gasification is clean energy. Other end products include fertilizers, fuels, and chemicals.
2. Non- thermal techniques
These are methods that do not depend mainly on heat to convert waste products into energy. They include;
Fermentation- the breakdown of organic matter into ethanol or alcohol
Anaerobic digestion- a method of biogas production where animal wastes are placed in airtight containers and acted upon by bacteria.
Mechanical biological treatment- this is a method of processing mixed household waste into usable energy and other forms of usable products.

Importance of waste to energy
Some of the benefits of waste to energy include;
- Reduces the amount of environmental degradation from landfills
- Lowers the risk of air, water and soil contamination caused by other methods of waste management
- It is a source of energy production
- Helps reduce the dependence on imported energy and the costs of transporting energy from other countries
- It is a cheap way of energy production as it eliminates transport costs and the cost of purchasing imported energy
Final Word
The waste to the energy industry has gone through several changes over the years. Most of these changes revolve around the development of new technologies. Different economies are looking to come up with ways of eliminating the use of landfills. Waste to energy techniques continues to evolve, while more than 50 percent of waste in the globe is being managed through garbage to energy methods like incineration.