There are several methods of waste disposal. Coincidentally, most of these methods involve the conversion of waste materials into usable energy. Some of the methods of waste conversion are thermal technologies. Such methods employ heating techniques. Thermal technologies include incineration, pyrolysis waste oil distillation, and thermal depolarization.
But note, the transformation of waste to energy is done in waste to energy plants. There are several wastes to energy plants in the industry. One of the most prominent plants is MoreGreen. This is a plant-based in china that was established in 2015. In less than half a decade, the plant has garnered business with different countries in the South Eastern region of Asia, China, South Korea, India, Turkey, and Russia. One of the most prominent facilities run by MoreGreen is the thermal depolymerization plant.
What is Thermal Depolymerization?
Depolymerization is a method of converting organic waste like biomass and plastic into light crude oil. In most cases, this process involves the use of hydrous pyrolysis. This Hydrous pyrolysis is the process through which organic compounds get heated in very high temperatures within water presence. The developers of this method of waste disposal and energy production, in many ways, mimic geological processes in which fossil fuels are produced. The application of thermal depolymerization in industries began in 1999. This breakthrough was a result of seven decades of research and experimentation on the topic.

The Process of Thermal Depolymerization
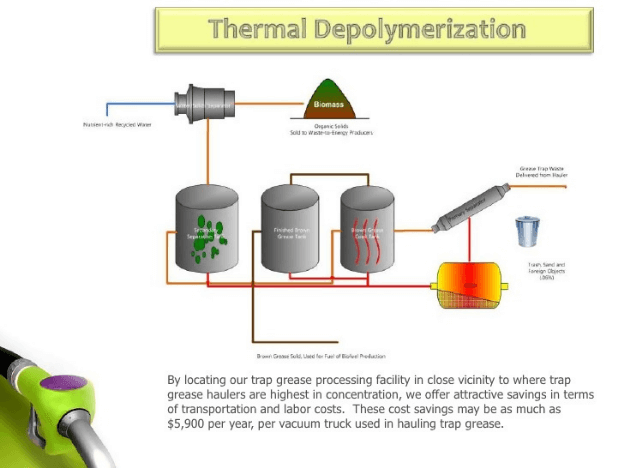
The first step in this process is the breaking down of biomass of organic wastes into small pieces. The small pieces of organic waste are then mixed with water and exposed to a heat of two hundred and fifty degrees Celsius. This occurs in a heating chamber where the residue is left for a minimum of fifteen minutes. While the waste heats up, a stem is produced. The waste stream causes a rise in the pressure in the machine to approximately six hundred pounds per square inch. At the end of the heating process, the pressure is exceptionally high, causing the water in the waste to evaporate.
Once the water is separated from the organic waste, a residue solid and crude hydrocarbon compounds are left behind. The residue is separated from the hydrocarbon elements. The hydrocarbons are then collected and transported to a refinement chamber. In this chamber, the hydrocarbons are heated at a temperature of five hundred degrees Celsius and sorted in the process of fractional distillation. The end products of the process of fractional distillation are naphthas (both heavy and light), gas oil, and kerosene. The gas oil is used in the production of varying grades of fuel oil.
The solid residue collected initially is not left without purpose. It is used as fertilizer, filters, soil fuel, and activated carbon in water treatment plants.

Final Word
Thermal depolymerization is applied in waste reduction and oil production. It is also beneficial in environmental conservation as it helps in the production of fuel resources that the world can benefit from. An unlimited number of fuel products can be obtained from the process of thermal depolymerization depending on the type of plant and the method employed.